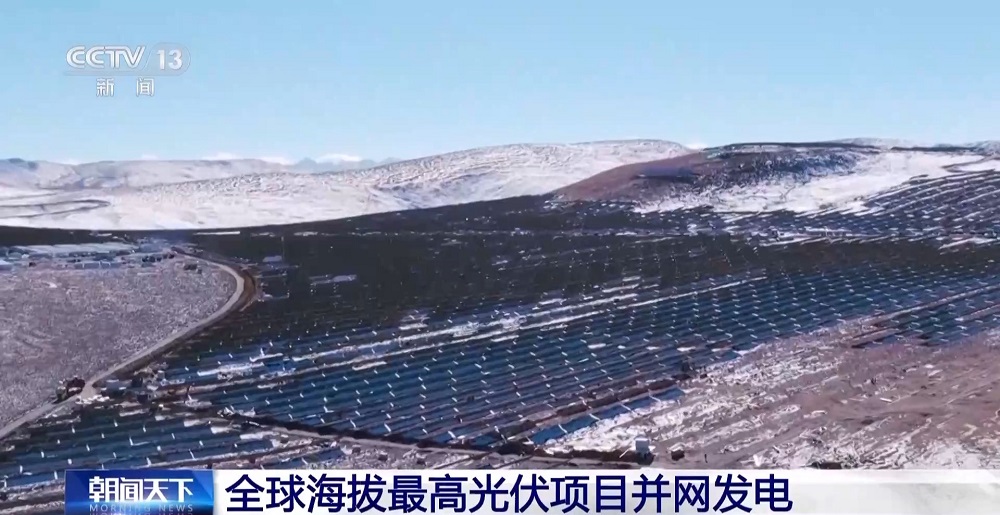
On December 14, the second phase of the Caipeng Solar Storage Power Station in Tibet officially started generating electricity. A total of 250,000 photovoltaic panels have been installed in the Shannan region of Tibet, with the project's highest elevation reached at 5,228 meters, making it currently the world's highest-altitude photovoltaic project (source: CCTV News App).
Photovoltaic cables were selected for their conductive materials, fully considering safety and stability. Tinned copper wire has become the preferred material for photovoltaic cables.
Clean energy helps locals meet their daily needs, often accompanied by the groundbreaking application of photovoltaic equipment in extreme outdoor environments: in plateaus, deserts, oceans, and other environments, with adverse conditions such as high temperatures, strong ultraviolet rays, extreme cold, humidity, and corrosiveness.
In 2017, China installed 3.46 million photovoltaic panels in the Kubuqi Desert, forming a "sand control belt," achieving full-capacity grid-connected power generation. The Kubuqi Desert is known for its large temperature differences between day and night and strong ultraviolet radiation, earning it the nickname "Sea of Death."
In 2019, the Bhadla Solar Power Plant in India was completed. The Bhadla region is sandy, dry, and arid, with average temperatures hovering between 46 to 48 degrees Celsius, frequently experiencing hot winds and sandstorms.
In October of this year, the world's first deep-sea floating photovoltaic demonstration project to be put into operation, the No. 3 offshore wind farm on the southern Shandong Peninsula, successfully generated power. The equipment was placed 30 kilometers offshore, in water depths of 30 meters, facing extreme ocean conditions with wave heights reaching 10 meters. The photovoltaic modules make direct contact with seawater through a film.

Building economically efficient photovoltaic projects represents an important goal and core competitiveness for all manufacturers in the industry chain. In fact, safe and stable photovoltaic systems depend on components that are not visible on the surface, such as the wiring system that connects photovoltaic modules and inverters. Choosing high-quality wire cores can avoid high maintenance costs and ensure the system's service life.
The choice of conductive materials for photovoltaic cables is crucial
Unlike ordinary power cables, cables used in photovoltaic systems need to endure long-term use in harsh outdoor environments, requiring characteristics such as ultraviolet resistance, heat resistance, cold resistance, and chemical corrosion resistance. They are mainly responsible for connecting solar panels, inverters, and the grid, transmitting the direct current generated by the solar panels and converting it into alternating current, which is then fed into the grid to provide clean energy for households, industries, and other fields.
The performance of the conductor material of photovoltaic cables directly impacts the safety and stability of photovoltaic systems. Common conductor structures include one or multiple strands, with material options like aluminum conductors, aluminum alloy conductors, bare copper wires, and tinned copper wires.
Aluminum conductor: Cheaper than copper material, it is lighter, reducing transportation costs. However, due to its low conductivity, high electrical loss, poor tensile strength, low corrosion resistance, and tendency for oxidized joints, aluminum-core photovoltaic cables are suitable for low-cost projects or temporary electricity use.
Aluminum alloy conductor: Its tensile strength is somewhat improved compared to pure aluminum conductors, with some products achieving an elongation rate of 30%. Unique alloy formulations and processing techniques result in better load-bearing and bending performance. However, it has lower corrosion resistance than aluminum, lower temperature resistance than copper, and a thermal expansion coefficient much higher than copper, sometimes even higher than aluminum.
Bare copper wire: Made of pure copper, it has good ductility, low resistivity, and low heat generation. Although costlier than aluminum, it is an excellent conductive material, widely used in automotive wire harness conductors, communication cable conductors, clean energy conductors, electromagnetic wire conductors, special cable conductors, and electronic appliance conductors.
Tinned copper wire: Tin is stable at room temperature and is the most economical and practical metal with the necessary properties. After drawing pure copper rods into wire, a layer of thin silver tin is plated on the copper wire's surface through a tinning process.
The following is a comparison of the main properties of various wires:
Parameter/Category | Aluminum Wire | Bare Copper Wire | Tinned Copper Wire |
Diameter | 2.6mm | 2.6mm | 2.6mm |
Plating Thickness | / | / | (1-20)μ |
Resistivity | ≤0.0282 | ≤0.0172 | ≤0.0176 |
Elongation | 18% | >30% | ≥25% |
As can be seen, due to the role of the tin coating, a dense oxide film forms on the copper surface, which has no substantial impact on resistivity and elongation, while enhancing oxidation resistance, making the material corrosion-resistant and easy to store.
When equipment is running, photovoltaic cables need to withstand the high temperatures generated by the panels during power generation. Facilities exposed long-term to outdoor environments also need to possess good weather resistance and excellent UV aging resistance. Additionally, in humid or acidic environments, they need to resist corrosion potentially caused by moisture and grounding chemicals. This is particularly important in marine environments, such as for marine photovoltaic connection cables, offshore oil drilling platforms, and wastewater treatment facilities, as saltwater is more corrosive than freshwater. Therefore, choosing tinned copper wire ensures that cables maintain their physical and chemical properties in harsh environments with humidity, high temperature, and dust, sustaining stable operation of the facilities.
For hard-to-reach locations such as underground or high-altitude spaces, using tinned copper wires in systems that are difficult to maintain or have high maintenance costs can ensure stable operation of the facilities while improving profitability.

The use of sustainable materials like copper wire and tinned copper wire will continue to expand
Copper wires are widely used in the electrical and electronics industries for the production of connecting wires, wire harnesses, and components, as well as vehicle wiring. With the increasing emphasis on environmental protection and green development, copper wire is favored for its recyclability and sustainability. The use of sustainable materials such as tinned copper wire is expected to continue to expand. According to data from Business Research Insights, the global tinned copper wire market size was USD 410 million in 2023 and is expected to reach USD 650 million by 2032, with a compound annual growth rate of 4.76% during the forecast period.
As one of professional tinned copper wire suppliers, Jintian Copper has established eight production bases globally, with specialized production facilities for bare copper wire, stranded wire, and tinned copper stranded wire products in Ningbo headquarters, Hangzhou Bay production base, Guangdong Jintian, and Chongqing Jintian.
The company imports first-class testing instruments and equipment from Germany, Japan, and the United States, and has built several globally leading production lines for continuous casting and rolling, Niehoff multi-head drawing machines, stranded wire, and tinned stranded wire automation lines. By integrating and applying information systems such as WMS (Warehouse Management System), MES (Manufacturing Execution System), and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition System), a digital production workshop is established to provide customers with professional tinned copper wire products and related services.
For more inquiries, feel free to leave a message or add our company service WeChat. We look forward to your communication!


 English
English 한국어
한국어 français
français Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español italiano
italiano العربية
العربية tiếng việt
tiếng việt Türkçe
Türkçe ไทย
ไทย 中文
中文